Electrical Contact Resistance (ECR) Testing for Nano-Scale Material Analysis)
Electrical contact resistance
Technical Notes
ECR Testing in Nano-Indentation, Wear, and Impact Tests
The multi-sensing capability of the multifunctional NanoTest™ Vantage™ nanomechanical test system is enhanced with the Electrical Contact Resistance (ECR) measurement module. The ECR module measures the electrical current and voltage between an electrically conductive indenter and the sample during any of the nano/micro mechanical measurements (nanoindentation, nano-scratch, nano-impact, nano-fretting, reciprocating nano-wear) possible in the NanoTest™ Vantage™.
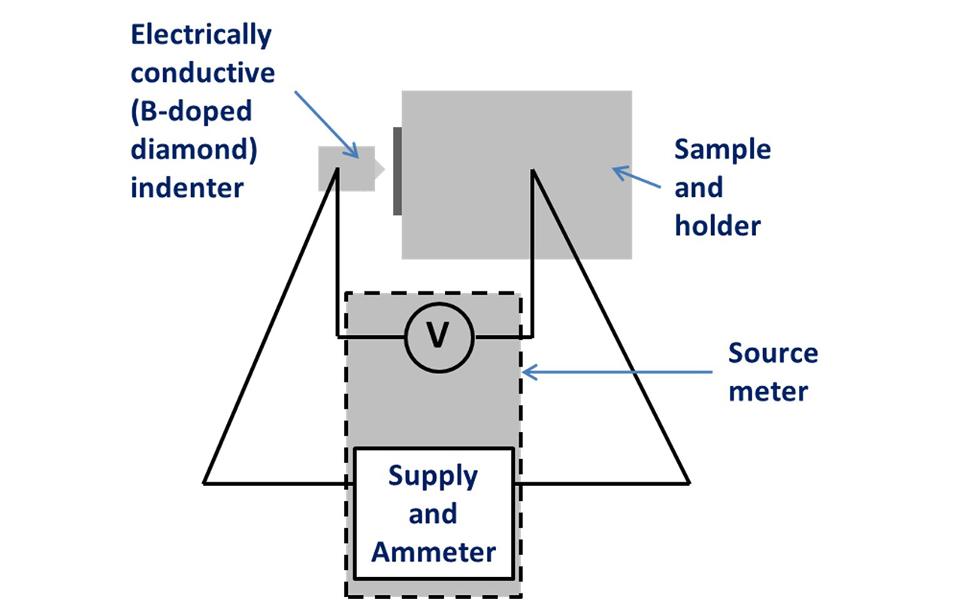
Electrically conductive probes such as metallic materials or Boron-doped diamond are required for ECR measurement. The conductive indenter creates an electrical circuit during a nano-scale contact (indentation, scratch, impact, fretting or nano-wear) shown schematically in the figure. Tests can be run in constant current or constant voltage modes.
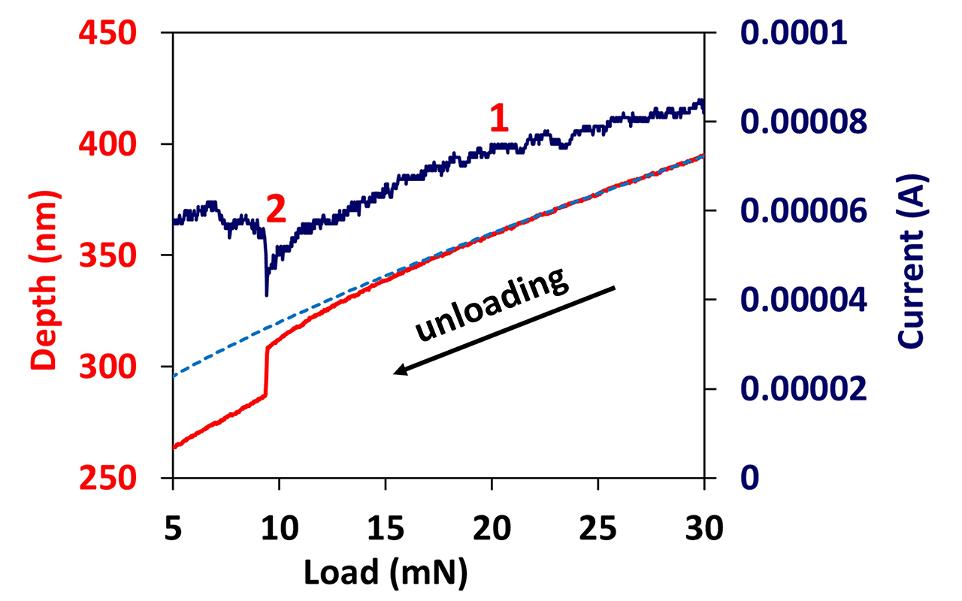
Silicon undergoes complex behaviour during indentation, with phase transformations and brittle fracture at higher load. ECR measurements using a Boron-doped diamond Berkovich indenter as the electrically conductive probe can provide additional information about the phase transformations that occur in loading and unloading.
Measurements on Si(100) show the initial deviation from elastic unloading associated with phase transformation begins (point 1) before the well-known “pop-out” event (point 2) that occurs with further unloading.
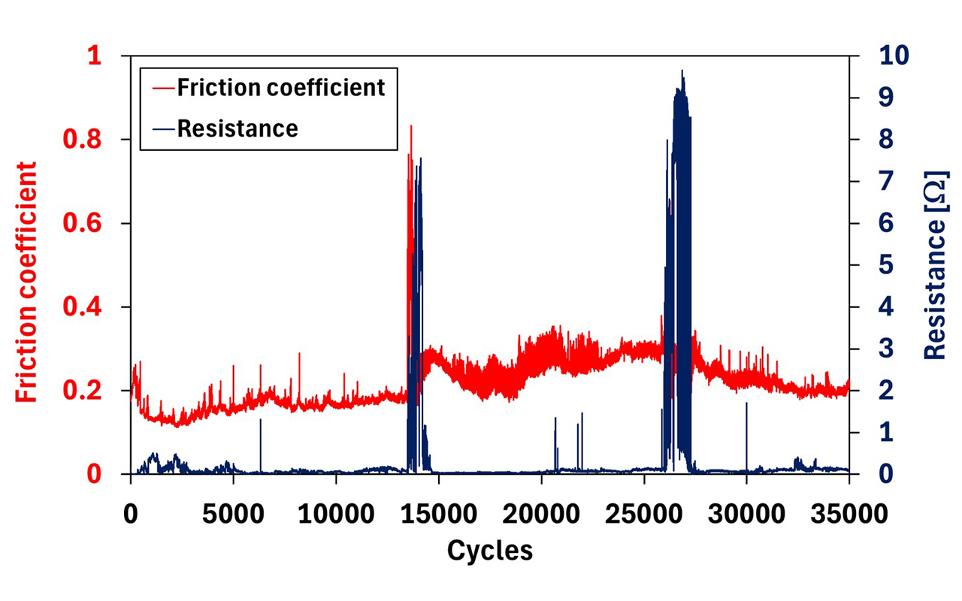
ECR measurement during reciprocating nano-wear tests provides unique insights into how surface topography and mechanical properties influence the friction, wear and endurance of sliding metallic connectors and multilayer coating systems.
Details of the complex failure mechanisms can be revealed by simultaneous monitoring of friction and ECR during the test.
Explore More
To further enhance your experience and understanding, we invite you to check out the following pages on our website that we believe are essential to your journey with us:
- High-Temperature Nanoindentation Testing for Advanced Material Characterization
- Advanced Nano Scratch and Wear Testing for Coatings and Materials
- Nano-Impact Testing for Advanced Material Performance in High-Stress Applications
These pages offer valuable insights and resources to help you achieve your goals.